We are excited to announce the publication of a ground-breaking research paper in the prestigious journal Physical Review X, presenting a novel method for detecting axions using particle accelerators. The experiment described in the paper was carried out by the JEDI (Juelich Electric Dipole moment Investigations) collaboration at the COSY synchrotron in Forschungszentrum Juelich, Germany, with contributors from the Department of Hadron Physics of our Faculty: prof. dr hab. Andrzej Magiera, dr Aleksandra Wrońska, and PhD student Swathi Karanth, who analyzed the data within her PhD project.
Axions, originally proposed to address the Charge Parity (CP) invariance problem in strong interaction, have emerged as promising candidates for Dark Matter. This new method is based `on the assumption that the Dark Matter particles induce oscillations to the spin of nucleons, with a frequency derived from their mass.
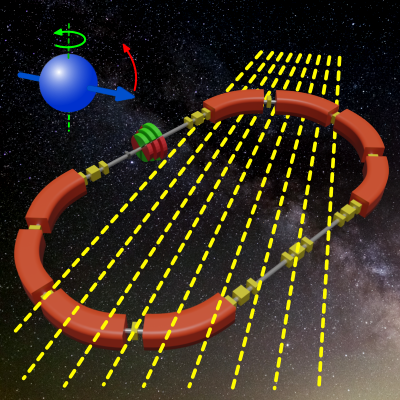
The experiment involved precise observations of the polarisation of the deuteron particle beam in the particle accelerator. The spin vectors experienced precession in the presence of the magnetic fields. By tuning the spin precession frequency, the scientists aimed to find resonance with the frequency induced by axion field. The utilisation of the particle accelerator provided significant advantage, as the relativistic momentum of the particles greatly enhanced the sensitivity compared to experiments conducted with particles at rest.
Although the experiment did not yield resonance signals indicative of the presence of axions, it successfully established new and improved constraints on the coupling between axion-like particles and ordinary matter. This research paves way for new avenues in the search of axions and towards our understanding of Dark Matter.

